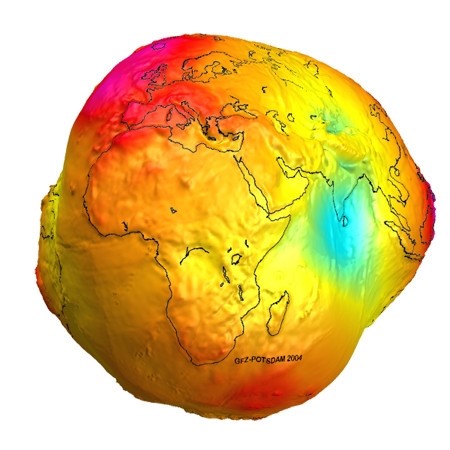
不规则的地球
地球其实不是圆的,当然也不是平的,地球虽是个球体,但是由于受到自转时的惯性及离心力的作用,他并非完美的圆形。所以地球最高点并不是珠穆朗玛峰,虽然其海拔有8848米,由于地球不是完美的球型,所以赤道附近的山峰其实离星空更近一些,因此地球最高点理论上是厄瓜多尔博拉索山(Mount Chimborazo),它的海拔虽然有6272米,却比珠峰”高”出2400米。
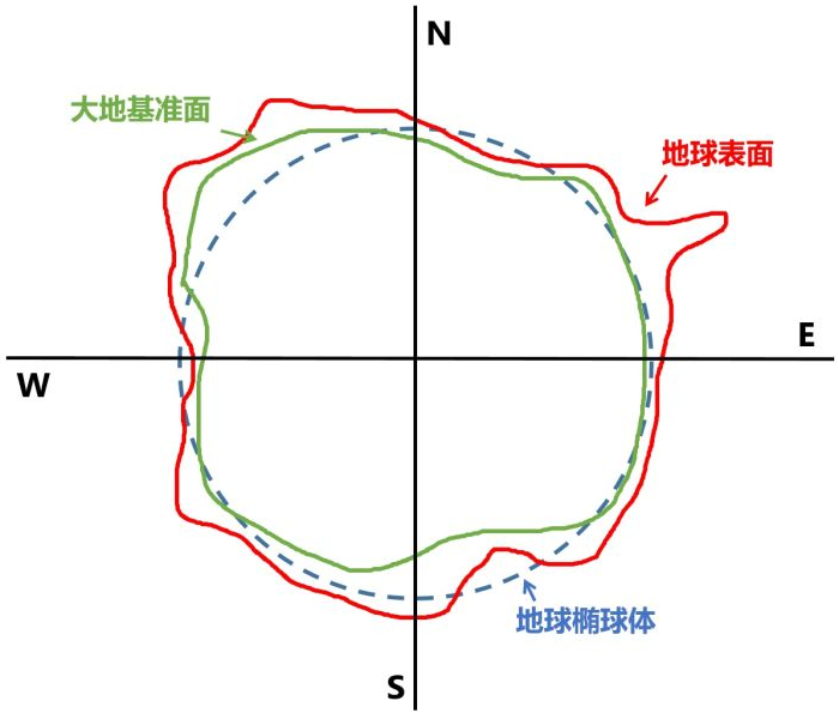
下图中红色实线圈为地球自然表面,由于地球自然表面坑坑洼洼、凹凸不平,所以在进行精准测量和定位的时候是不能直接用数据公式来拟合地球表面的。这时,用一个可以近似表示地球表面的规则的椭圆(如上图中的蓝色虚线框所示)来进行地球表面的定位和测量,这个规则的三维球面就是地球椭球体。但是,地球表面高低起伏不平,造成地球椭球体与地球自然表面在有的地方能够十分贴合,在有的地方则不是很贴合,这会造成测量及定位地误差。所以,需要在地球椭球体以及地球自然表面之间加一层中间层,使其能够尽量贴合真实的地球表面,那这中间层就是大地基准面(如图中绿色实线圈所示),其可以理解为在特定区域内与地球自然表面极为吻合的椭球体。
地球上各个地方的地理位置及环境都是独一无二的,为了满足当地测量及定位的精度要求,全世界的地理学家们建立了无数个适合当地的大地基准面。地理坐标系统就是由大地基准面衍生而来的,其是使用三维球面来定义地球表面位置,以实现通过经纬度对地球表面点位引用的坐标系。一个地理坐标系包括角度测量单位、本初子午线和基准面三部分。一个大地基准面可以对应多个地理坐标系统,而一个地理坐标系统只能对应一个大地基准面。同一个坐标点在不同地理坐标系的地图上,会落在不同的区域;同一个地点获取不同地理坐标系下的坐标数据,值不相同。因此,在地图制图以及空间分析之前,先要了解坐标点以及地图的地理坐标系统。
经纬度小数位数对精度的影响
通过百度或者Google,可以获得如下信息:
在纬度相等的情况下:
- 经度每隔0.000001度,距离相差约1米
- 经度每隔0.00001度,距离相差约10米
- 经度每隔0.0001度,距离相差约100米
- 经度每隔0.001度,距离相差约1000米
- 经度每隔0.01度,距离相差约10000米
在经度相等的情况下:
- 纬度每隔0.000001度,距离相差约1.1米
- 纬度每隔0.00001度,距离相差约11米
- 纬度每隔0.0001度,距离相差约111米
- 纬度每隔0.001度,距离相差约1113米
- 纬度每隔0.01度,距离相差约11132米
但是上诉的答案是否是正确的呢?我们先来了解下地球的一些基本信息:
- 地球的赤道半径= 6378.1公里
- 地球的极半径= 6356.8公里
- Latitude的范围是:-90到+90
- Longitude的范围:-180到+180
- 地球参考球体的周长:68米
经纬度划分规则如下图:
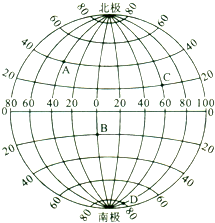
从上述的图片中可以看到,经度和纬度的划分规则是不一样的。所以网上搜索的经纬度经度对于精度的影响并不正确的。
- 纬度每格1度影响的距离= 极半径*π/180=110.95km
- 经度每隔1度影响的距离(赤道)= 赤道半径*π/180=111.32km,维度越靠近南北极,影响的距离越小。
经纬度距离计算方法
基于球面模型的地理空间距离计算:
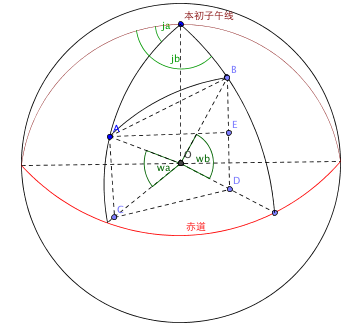
该模型将地球看成圆球,假设地球上有A(ja,wa),B(jb,wb)两点(注:ja和jb分别是A和B的经度,wa和wb分别是A和B的纬度),A和B两点的球面距离就是AB的弧长,AB弧长=R*角AOB(注:角AOB是A跟B的夹角,O是地球的球心,R是地球半径,约为6367000米)。如何求出角AOB呢?可以先求AOB的最大边AB的长度,再根据余弦定律可以求夹角。用公式表示为:
$$S=2\times\arcsin(\sqrt{\sin^2(\frac{a}{2})+\cos(Lat1)\times\cos(lat2)\times sin^2(\frac{b}{2})})\times6378.137$$
Google maps中的距离计算代码:
private const double EARTH_RADIUS = 6378.137;
private static double rad(double d)
{
return d * Math.PI / 180.0;
}
public static double GetDistance(double lat1, double lng1, double lat2, double lng2)
{
double radLat1 = rad(lat1);
double radLat2 = rad(lat2);
double a = radLat1 - radLat2;
double b = rad(lng1) - rad(lng2);
double s = 2 * Math.Asin(Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(Math.Sin(a/2),2) + Math.Cos(radLat1) * Math.Cos(radLat2) * Math.Pow(Math.Sin(b/2),2)));
s = s * EARTH_RADIUS;
s = Math.Round(s * 10000) / 10000;
return s;
}
由于Google Map主要使用的是WGS-84坐标系,经纬度相对标准,但对于国内的火星坐标(GCJ-02)和百度坐标(BD-09)经纬度之间距离的计算是否存在差异呢?我们从百度地图中的距离计算代码来分析:
var j = void 0,
p = null,
H.prototype.nb = function(a) {
return a && this.lat == a.lat && this.lng == a.lng
};
getDistance: function(a, b) {
if (a && b) {
if (a.nb(b)) return 0;
var c = 0,
c = R.To(a, b);
if (c === p || c === j) c = 0;
return c
}
},
nb: function(a) {
return !(a instanceof eb) || this.xj() ? q : this.se().nb(a.se()) && this.of().nb(a.of())
},
function R() {}
R.prototype = new gc;
x.extend(R, {
To: function(a, b) {
if (!a || !b) return 0;
a.lng = this.ND(a.lng, -180, 180);
a.lat = this.RD(a.lat, -74, 74);
b.lng = this.ND(b.lng, -180, 180);
b.lat = this.RD(b.lat, -74, 74);
return this.Re(this.Sk(a.lng), this.Sk(b.lng), this.Sk(a.lat), this.Sk(b.lat))
},
Re: function(a, b, c, d) {
return this.jP * Math.acos(Math.sin(c) * Math.sin(d) + Math.cos(c) * Math.cos(d) * Math.cos(b - a))
},
jP: 6370996.81,
RD: function(a, b, c) {
b != p && (a = Math.max(a, b));
c != p && (a = Math.min(a, c));
return a
},
ND: function(a, b, c) {
for (; a > c;) a -= c - b;
for (; a< b;) a += c - b;
return a
}
Sk: function(a) {
return Math.PI * a / 180
},
});
上述代码用Python重写后:
def get_distance_bd09(point_a, point_b):
"""
算法来源:http://developer.baidu.com/map/jsdemo.htm#a6_1
:param pointA: {lat:29.490295, lng:106.486654}
:param pointB: {lat:29.615467, lng:106.581515}
:return: 米
"""
R = 6370996.81 #球半径
if (point_a and point_b):
if point_a["lat"] == point_b["lat"] and point_a["lng"] == point_b["lng"]:
distance = 0
else:
a_lat = point_a["lat"] * math.pi / 180
a_lng = point_a["lng"] * math.pi / 180
b_lat = point_b["lat"] * math.pi / 180
b_lng = point_b["lng"] * math.pi / 180
#print(a_lng, b_lng, a_lat, b_lat)
distance = R * math.acos(math.sin(a_lat) * math.sin(b_lat) + math.cos(a_lat) * math.cos(b_lat) * math.cos(b_lng - a_lng))
return distance
此计算方法与常用的haversine算法完全一致:
from math import radians, sin, cos, asin, sqrt
def haversine(latlon1, latlon2):
lat1, lon1 = latlon1
lat2, lon2 = latlon2
lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2 = map(radians, [lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2])
dlon = lon2 - lon1
dlat = lat2 - lat1
a = sin(dlat/2)**2 + cos(lat1) * cos(lat2) * sin(dlon/2)**2
c = 2 * asin(sqrt(a))
r = 6370996.81 #球半径
return c * r
也就是说百度忽略了BD-09坐标系带来的经纬度偏移。
为方便使用也可以开发数据库自定义函数(以下代码适用于SQLServer):
USE [testdb]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE FUNCTION [dbo].[f_GetDistance]
(
@GPSLng DECIMAL(12,6),
@GPSLat DECIMAL(12,6),
@Lng DECIMAL(12,6),
@Lat DECIMAL(12,6)
)
RETURNS DECIMAL(12,4)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @result DECIMAL(12,4)
IF @GPSLng = @Lng AND @GPSLat = @Lat
BEGIN
SELECT @result = 0
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SELECT @result = 6370996.81 * ACOS(SIN(@GPSLat/180*PI()) * SIN(@Lat/180*PI()) + COS(@GPSLat/180*PI()) * COS(@Lat/180*PI()) * COS((@GPSLng - @Lng)/180*PI()))
END
RETURN @result
END
经纬度距离计算优化
问题:给定1万个POI点,迅速寻找出其1000米以内的其他POI点。解决此问题的关键是减少计算的复杂度,如果用最原始的方法,需要计算的次数为$n^2$。
方案一:Geohash法
将所有经纬度转化为特定精度的GeoHash值,再对同一Geohash内的内进行两两比较,以此减少计算复杂度。
存在问题:GeoHash的划分方式导致了其必产生边界问题(相邻的两个POI被划分到了不同的区域)
解决方案:将Geohash内的POI与Geohash的另外8个邻居中的POI再进行两两计算。由于涉及网格间的计算,程序的复杂度也会相应增加。
方案二:UberH3法
同上面的Geohash法类似,但相比Geohash法会更好一些:
- UberH3网格精度更高一些
- UberH3为六边形网格,更接近圆
- UberH3提供Ring方法,可以按照设定的K值获取中心网格周边距离第K个网格。
方案三:经纬度精度值限制法
根据上面提到的经纬度规则,可知:
- 纬度每格1度影响的距离= 极半径*π/180=110.95km
- 经度每隔1度影响的距离(赤道)= 赤道半径*π/180=111.32km,维度越靠近南北极,影响的距离越小。
在此基础上可以将两两比较的笛卡尔积过滤掉大部分:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([{'item_id':1234, 'lat':39.93607, 'lon':116.42394},
{'item_id':1235, 'lat':39.93526, 'lon':116.42590},
{'item_id':1236, 'lat':39.92969, 'lon':116.42961}])
df['tmp'] = 1
df = pd.merge(df, df, on='tmp')
df = df[df.item_id_x != df.item_id_y]
df = df[(abs(df['lat_x'] - df['lat_y']) < 0.02) & (abs(df['lng_x'] - df['lng_y']) < 0.02)]
方案四:简化经纬度计算公式
由于要计算的距离范围非常的小,我们可以将球面上的经线和纬线看成是垂直的。如图:
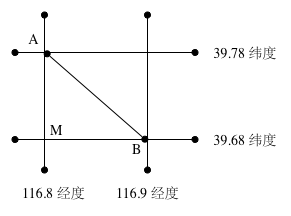
想要计算AB两个点距离$D=\sqrt{\text{AM}^2+\text{BM}^2}$,转化为Python代码为:
from math import radians, cos, sqrt
def haversine_hack(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2):
lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2 = map(radians, [lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2])
dx = lon2 - lon1 #经度差值
dy = lat2 - lat1 #纬度差值
b = (lat1 + lat2) / 2 #平均纬度
r = 6370996.81 #球半径
lx = dx * r * cos(b) #东西距离
ly = dy * r #南北距离
return sqrt(lx**2 + ly**2)
简化公式与标准公式的对比可知:在距离较小情况下计算出来的值相差不大。
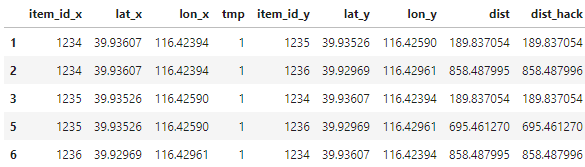
df['dist'] = df.apply(lambda row: haversine(row['lat_x'], row['lon_x'], row['lat_y'], row['lon_y']), axis=1) df['dist_hack'] = df.apply(lambda row: haversine_hack(row['lat_x'], row['lon_x'], row['lat_y'], row['lon_y']), axis=1)
参考链接: