文本分析是机器学习算法的主要应用领域。由于大部分机器学习算法只能接收固定长度的数值型矩阵特征,导致文本字符串等并不能直接被使用,针对此问题 Scikit-Learn 提供了将文本转化为数值型特征的方法,今天就一起来学习下。
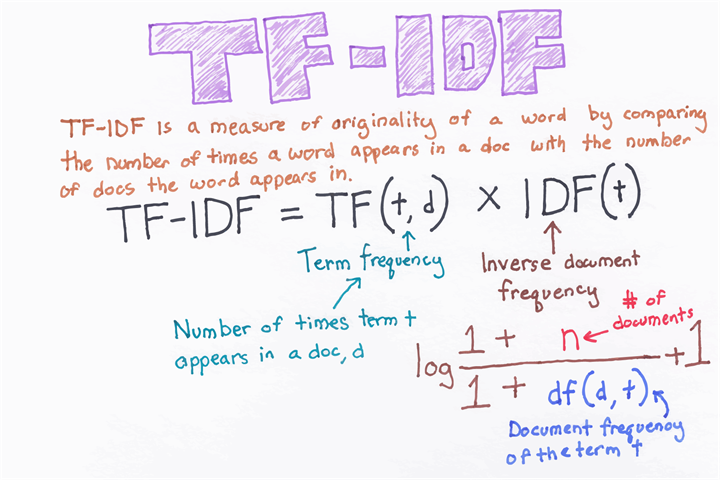
Scikit-Learn 中的 sklearn.feature_extraction.text 提供了将文本转化为特征向量的工具:
- CountVectorizer():将文本转化为词频矩阵
- TfidfTransformer():将 CountVectorizer() 词频矩阵转化为 tf-idf 矩阵
- TfidfVectorizer():将文本直接转化为 TF-IDF 矩阵
- HashingVectorizer():将文本转化为 Hash 矩阵
CountVectorizer
CountVectorizer 是通过 fit_transform 函数将文本中的词语转换为词频矩阵,矩阵元素 a[i][j] 表示 j 词在第 i 个文本下的词频。即各个词语出现的次数,通过 get_feature_names() 可看到所有文本的关键字,通过 toarray() 可看到词频矩阵的结果。
示例:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
corpus = [
'This is the first document.',
'This is the second second document.',
'And the third one.',
'Is this the first document?',
]
vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
count = vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
print(vectorizer.get_feature_names())
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)
print(count.toarray())
# 输出
# ['and', 'document', 'first', 'is', 'one', 'second', 'the', 'third', 'this']
# {'this': 8, 'is': 3, 'the': 6, 'first': 2, 'document': 1, 'second': 5, 'and': 0, 'third': 7, 'one': 4}
# [[0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]
# [0 1 0 1 0 2 1 0 1]
# [1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0]
# [0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]]
class sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer(input=’content’, encoding=’utf-8’, decode_error=’strict’, strip_accents=None, lowercase=True, preprocessor=None, tokenizer=None, stop_words=None, token_pattern=’(?u)\b\w\w+\b’, ngram_range=(1, 1), analyzer=’word’, max_df=1.0, min_df=1, max_features=None, vocabulary=None, binary=False, dtype=<class ‘numpy.int64’>)
参数说明:
- input: string {‘filename’, ‘file’, ‘content’}
- 如果 ‘filename’,作为参数传递以适合的序列预期是需要读取来获取要分析的原始内容的文件名列表。
- 如果 ‘file’,序列项必须有一个 ‘read’ 方法(类文件对象),被调用来获取内存中的字节。
- 否则,预期输入是序列字符串或字节项目预计将被直接分析。
- encoding: string, ‘utf-8’ by default.
- 如果给出字节或文件进行分析,则使用此编码进行解码。
- decode_error: {‘strict’, ‘ignore’, ‘replace’}
- 指示如果给出一个字节序列来分析包含不是给定编码的字符,该怎么做。默认情况下,它是 ‘strict’,这意味着会引发 UnicodeDecodeError。其他值是“ignore”和“replace”。
- strip_accents: {‘ascii’, ‘unicode’, None}
- 是否在预处理步骤中删除重音符号。’ascii’ 是一种快速方法,仅适用于具有直接 ASCII 映射的字符。’unicode’ 是一个适用于任何字符的稍慢的方法。None(默认)什么也不做。
- lowercase: boolean, True by default
- 在令牌标记前转换所有的字符为小写
- preprocessor: callable or None (default)
- 覆盖预处理(字符串转换)阶段,同时保留 tokenizing 和 n-grams 生成步骤。
- tokenizer: callable or None (default)
- 重写字符串标记化步骤,同时保留预处理和 n-grams 生成步骤。
- 只适用于 analyzer == ‘word’
- stop_words: string {‘english’}, list, or None (default)
- 如果是字符串,则将其传递给 _check_stop_list,并返回相应的停止列表。’english’ 是目前唯一支持的字符串值。
- 如果一个列表,该列表被假定为包含停止词,所有这些都将从生成的令牌中删除。仅适用如果。analyzer == ‘word’
- 如果没有,将不会使用停止的单词。max_df 可以设置为 [0.7, 1.0] 范围内的值,以根据术语的语料库文档频率自动检测和过滤停止词。
- token_pattern: string
- 正则表达式,默认筛选长度 >= 2 的字母和数字混合字符(标点符号被完全忽略并始终被视为标记分隔符)。仅在 analyzer == ‘word’ 使用时才使用。
- ngram_range: tuple (min_n, max_n)
- 不同 n 值的 n 值范围的下边界和上边界被提取。将使用所有 n 值,使得 min_n<= n<= max_n。
- analyzer: string, {‘word’, ‘char’, ‘char_wb’} or callable
- 特征是否应由单词或字符 n-gram 组成。选项 ‘char_wb’ 仅从字边界内的文本创建字符 n-gram; 单词边缘的 n-grams 用空格填充。
- 如果通过可调用,它将用于从原始未处理输入中提取特征序列。
- max_df: float in range [0.0, 1.0] or int, default=1.0
- 当构建词汇表时,严格忽略高于给出阈值的文档频率的词条,语料指定的停用词。如果是浮点值,该参数代表文档的比例,整型绝对计数值,如果词汇表不为 None,此参数被忽略。
- min_df: float in range [0.0, 1.0] or int, default=1
- 当构建词汇表时,严格忽略低于给出阈值的文档频率的词条,语料指定的停用词。如果是浮点值,该参数代表文档的比例,整型绝对计数值,如果词汇表不为 None,此参数被忽略。
- max_features: int or None, default=None
- 如果不为 None,构建一个词汇表,仅考虑 max_features
- 按语料词频排序,如果词汇表不为 None,这个参数被忽略
- vocabulary: Mapping or iterable, optional
- 也是一个映射(Map)(例如,字典),其中键是词条而值是在特征矩阵中索引,或词条中的迭代器。如果没有给出,词汇表被确定来自输入文件。在映射中索引不能有重复,并且不能在0到最大索引值之间有间断。
- binary: boolean, default=False
- 如果未 True,所有非零计数被设置为1,这对于离散概率模型是有用的,建立二元事件模型,而不是整型计数
- dtype: type, optional
- 由 fit_transform()或 transform()返回的矩阵的类型。
属性:
- vocabulary_:dict
- 术语到特征索引的映射。
- stop_words_:set
- 因以下原因而被忽略的术语:
- 出现在太多文件中(max_df)
- 出现在文件太少(min_df)
- 被特征选择切断(max_features)
- 因以下原因而被忽略的术语:
方法:
- build_analyzer(self) Return a callable that handles preprocessing and tokenization
- build_preprocessor(self) Return a function to preprocess the text before tokenization
- build_tokenizer(self) Return a function that splits a string into a sequence of tokens
- decode(self, doc) Decode the input into a string of unicode symbols
- fit(self, raw_documents[, y]) 主要作用就是 load 数据,并进行相应计算.
- transform(self, raw_documents) 主要作用是将数据转化为 matrix 形式
- fit_transform(self, raw_documents[, y]) 将 fit 和 transform 两个步骤放在一起
- get_feature_names(self) 获取所有 features,即关键字列表
- get_params(self[, deep]) Get parameters for this estimator.
- get_stop_words(self) Build or fetch the effective stop words list
- inverse_transform(self, X) Return terms per document with nonzero entries in X.
- set_params(self, **params) Set the parameters of this estimator.
TfidfTransformer
TfidfTransformer 是统计 CountVectorizer 中每个词语的 tf-idf 权值。
示例:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfTransformer corpus = [ 'This is the first document.', 'This is the second second document.', 'And the third one.', 'Is this the first document?', ] vectorizer = CountVectorizer() transformer = TfidfTransformer() count = vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus) tfidf_matrix = transformer.fit_transform(count) print(tfidf_matrix.toarray()) #输出 #[[0. 0.43877674 0.54197657 0.43877674 0. # 0.35872874 0. 0.43877674] #[0. 0.27230147 0. 0.27230147 0.85322574 # 0.22262429 0. 0.27230147] #[0.55280532 0. 0. 0. 0.55280532. # 0.28847675 0.55280532.] #[0. 0.43877674 0.54197657 0.43877674 0. # 0.35872874 0. 0.43877674]]
class sklearn.feature_extraction.text.TfidfTransformer(norm=’l2’, use_idf=True, smooth_idf=True, sublinear_tf=False)
参数:
- norm: ‘l1’, ‘l2’ or None, optional (default=’l2’)
- 是否针对数据做 normalization,None 表示不做 normalization
- use_idf: boolean (default=True)
- 是否使用 idf,如果为 False,则退化为简单的词频统计
- smooth_idf: boolean (default=True)
- 通过加1到文档频率平滑 idf 权重,为防止除零,加入一个额外的文档
- sublinear_tf: boolean (default=False)
- 应用线性缩放 TF,如果为 True,则使用 1+log(tf) 来代替 tf
属性:
- idf_: array, shape (n_features)
- The inverse document frequency (IDF) vector; only defined if use_idf is True.
方法:
- fit(self, X[, y]) Learn the idf vector (global term weights)
- transform(self, X[, copy]) Transform a count matrix to a tfor tf-idf representation
- fit_transform(self, X[, y]) Fit to data, then transform it.
- get_params(self[, deep]) Get parameters for this estimator.
- set_params(self, **params) Set the parameters of this estimator.
- transform(self, X[, copy]) Transform a count matrix to a tfor tf-idf representation
TfidfVectorizer
将原始文档的集合转化为 tf-idf 特性的矩阵,相当于 CountVectorizer 配合 TfidfTransformer 使用的效果。即 TfidfVectorizer 类将 CountVectorizer 和 TfidfTransformer 类封装在一起。
示例:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
corpus = [
'This is the first document.',
'This is the second second document.',
'And the third one.',
'Is this the first document?',
]
tfidf_vec = TfidfVectorizer()
tfidf_matrix = tfidf_vec.fit_transform(corpus)
print(tfidf_vec.get_feature_names())
print(tfidf_vec.vocabulary_)
print(tfidf_matrix.toarray())
# 输出
# ['and', 'document', 'first', 'is', 'one', 'second', 'the', 'third', 'this']
# {'this': 8, 'is': 3, 'the': 6, 'first': 2, 'document': 1, 'second': 5, 'and': 0, 'third': 7, 'one': 4}
# [[0. 0.43877674 0.54197657 0.43877674 0. 0.
# 0.35872874 0. 0.43877674]
# [0. 0.27230147 0. 0.27230147 0. 0.85322574
# 0.22262429 0. 0.27230147]
# [0.55280532 0. 0. 0. 0.55280532 0.
# 0.28847675 0.55280532 0. ]
# [0. 0.43877674 0.54197657 0.43877674 0. 0.
# 0.35872874 0. 0.43877674]]
HashingVectorizer
单词频率和权重是很有用的,但是当词汇表变得很大时,以上两种方法就会出现局限性。反过来,这将需要巨大的向量来编码文档,并对内存要求很高,而且会减慢算法的速度。一种很好的方法是使用单向哈希方法来将单词转化成整数。好处是该方法不需要词汇表,可以选择任意长的固定长度向量。缺点是哈希量化是单向的,因此无法将编码转换回单词(对与许多有监督的学习任务来说或许并不重要)。
HashingVectorizer类实现了这一方法,所以可以使用它对单词进行连续哈希量化,然后按需求词条化和编码文档。下面是对单一文档使用HashingVectorizer进行编码的示例。我们选择了一个固定长度为20的任意向量。这个值对应哈希函数的范围,小的值(例如20)可能会导致哈希碰撞。在之前的计算机科学课程中,我们介绍过一些启发式算法,可以根据估计的词汇量来选择哈希长度和碰撞概率。
注意这种量化方法不要求调用函数来对训练数据文件进行拟合。相反,在实例化之后,它可以直接用于编码文档。
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import HashingVectorizer text = ["The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog."] vectorizer = HashingVectorizer(n_features=20) vector = vectorizer.transform(text) print(vector.shape) print(vector.toarray())
运行该示例代码可以把样例文档编码成一个含有20个元素的稀疏矩阵。编码文档的值对应于正则化的单词计数,默认值在-1到1之间,但是可以修改默认设置,然后设置成整数计数值。
(1, 20) [[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.33333333 0. -0.33333333 0.33333333 0. 0. 0.33333333 0. 0. 0. -0.33333333 0. -0.66666667 0. ]]
参考链接:

很佩服作者将很多知识进行了梳理,文章也写得很清晰,希望能一直看到你的更新!