文章内容如有错误或排版问题,请提交反馈,非常感谢!
项目需求
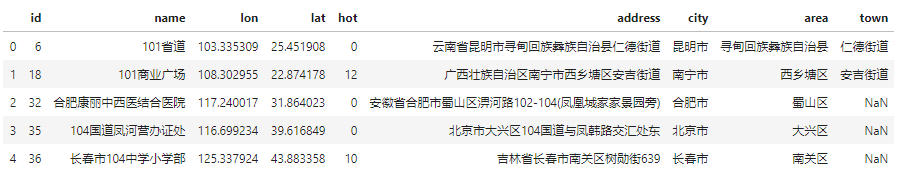
去除从地图网站抓取的POI数据中的重复数据。示例数据如下:
思考逻辑
POI去重问题,并非简单的文本匹配,按照编辑距离去做,可能会走到沟里去。
不同地方有相同名字的POI点,如:
- 行政管理中心
- 人民桥
- 中央公园
- …
解决方案:通过经纬度限定区域,在限定区域内找出重复POI。初步方案用Geohash的精度做区域限定。
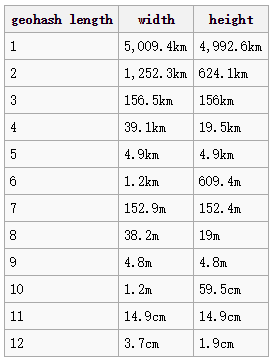
选定的精度是5,如果担心出现边界问题,可采用缩放精度解决。
相同区域内,可能存在两个极为相似的POI点,如:
- 苏州工业园区第七中学
- 苏州工业园区第八中学
解决方案:分词后计算TF-IDF,给予每个词不同权重后进行比较。
代码实现
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import geohash # pip install python-geohash
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sparse_dot_topn import awesome_cossim_topn
import pkuseg
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from multiprocessing import Pool
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost/hackathon")
def step_1():
"""数据准备"""
seg = pkuseg.pkuseg()
stopwords = [',', '\n', '(', ')', '|', '-', '/']
def cut_word(content):
text = seg.cut(str(content))
new_text = []
for w in text:
if w not in stopwords:
new_text.append(w)
return "".join(new_text)
# 加载原始数据
poi_data = pd.read_csv("data/poi_data.txt", sep='\t',
names=['id', 'name', 'lon', 'lat', 'hot', 'address', 'city', 'area', 'town'])
# 删除经纬度错误数据
poi_data = poi_data[
(poi_data['lat'] <= 90.0) & (poi_data['lat'] >= -90.0) & (poi_data['lon'] <= 180) & (poi_data['lon'] >= -180)]
# 新增GEOHASH列,取精度为5,即误差范围为4.9km左右
poi_data["geohash"] = np.vectorize(geohash.encode)(poi_data['lat'], poi_data['lon'], precision=5)
# 新增分词后字段
poi_data["name_cut"] = np.vectorize(cut_word)(poi_data['name'])
poi_data["address_cut"] = np.vectorize(cut_word)(poi_data['address'])
poi_data['name_address_cut'] = poi_data['name_cut'] + ' ' + poi_data['address_cut']
# 保存数据到pkl文件
poi_data.to_pickle("./poi_data.pkl")
def step_2():
"""相似度计算,并存入数据库"""
poi_data = pd.read_pickle("./poi_data.pkl")
def get_matches_df(sparse_matrix, df_name_vactor, top=500):
name_vector = df_name_vactor['name_address_cut']
non_zeros = sparse_matrix.nonzero()
sparserows = non_zeros[0]
sparsecols = non_zeros[1]
nr_matches = top if top < sparse_matrix.shape[0] else sparse_matrix.shape[0]
left_side = np.empty([nr_matches], dtype=object)
right_side = np.empty([nr_matches], dtype=object)
left_id = np.empty([nr_matches], dtype=object)
right_id = np.empty([nr_matches], dtype=object)
similairity = np.zeros(nr_matches)
for index in range(0, nr_matches):
left_side[index] = name_vector[sparserows[index]]
right_side[index] = name_vector[sparsecols[index]]
left_id[index] = df_name_vactor.iloc[sparserows[index]]['id']
right_id[index] = df_name_vactor.iloc[sparsecols[index]]['id']
similairity[index] = sparse_matrix.data[index]
return pd.DataFrame({'left_side': left_side,
'right_side': right_side,
'left_id': left_id,
'right_id': right_id,
'similarity': similairity})
def pair_insert(ghash):
poi_area = poi_data[poi_data["geohash"] == ghash].reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word', sublinear_tf=True)
# vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word', token_pattern="(?u)\\b\\w+\\b", sublinear_tf=True)
tf_idf_matrix = vectorizer.fit_transform(poi_area['name_address_cut'])
matches = awesome_cossim_topn(tf_idf_matrix, tf_idf_matrix.transpose(), 5)
matches_df = get_matches_df(matches, poi_area)
matches_df = matches_df[matches_df['similarity'] < 0.99999]
print(matches_df.shape)
matches_df['left_id'] = matches_df['left_id'].astype('int')
matches_df['right_id'] = matches_df['right_id'].astype('int')
matches_df['similarity'] = matches_df['similarity'].astype('float')
matches_df.to_sql(con=engine, name='pair_result', if_exists='append')
pool = Pool(8)
pool.map(pair_insert, poi_data["geohash"].unique())
pool.close()
pool.join()
if __name__ == "__main__":
step_1()
step_2()
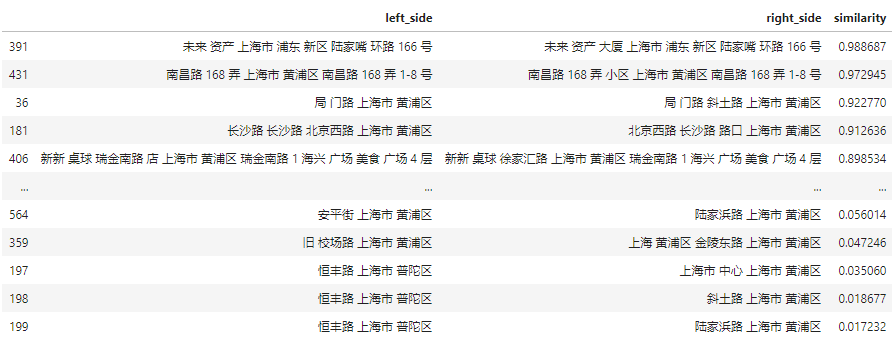
按区域进行匹配示例:
df_idf = pd.DataFrame(vectorizer.idf_, index=vectorizer.get_feature_names(), columns=["idf_weights"]) df_idf.sort_values(by=['idf_weights'])
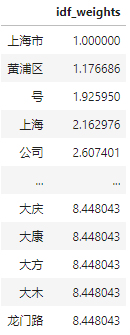
每个POI分词后的TF-IDF:
test = df["name_address_cut"][:2].tolist()
idf_dict = dict(zip(vectorizer.get_feature_names(), vectorizer.idf_))
for i in range(len(test)):
print(test[i])
for word in test[i].split(" "):
try:
print(word, idf_dict[word])
except:
pass
print("")

最终结果: