文章内容如有错误或排版问题,请提交反馈,非常感谢!
在 Python 中总共有两种字符串格式化方案,一种是在 Python 2.6 之前就有的 % 运算符,另外一个是从 Python 2.6 开始新增的一种格式化字符串函数 str.format()。
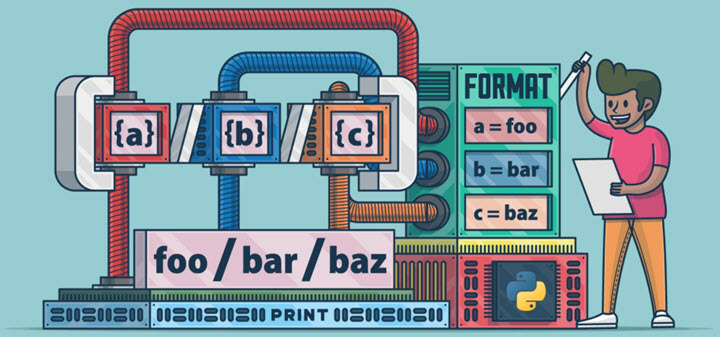
% 格式化工具
熟悉 C 语言 printf() 函数的同学会很容易学会 % 格式化工具。print() 函数使用以 % 开头的转换说明符对各种类型的数据进行格式化输出:
整数的输出:
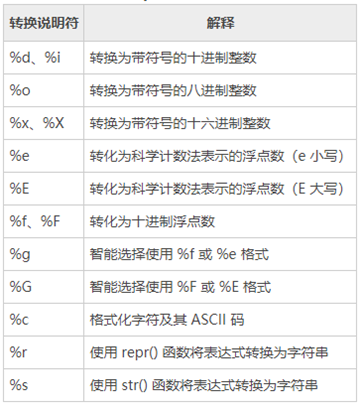
- %o —— oct 八进制
- %d —— dec 十进制
- %x —— hex 十六进制
浮点数的输出:
- %f —— 保留小数点后面六位有效数字。%.3f,保留 3 位小数位
- %e —— 保留小数点后面六位有效数字,指数形式输出。%.3e,保留 3 位小数位,使用科学计数法
- %g —— 在保证六位有效数字的前提下,使用小数方式,否则使用科学计数法。%.3g,保留 3 位有效数字,使用小数或科学计数法
字符串输出:
- %s —— 输出字符串
- %10s —— 右对齐,占位符 10 位
- %-10s —— 左对齐,占位符 10 位
- %.2s —— 截取 2 位字符串
- %10.2s —— 10 位占位符,截取两位字符串
print('%o' % 20)
print('%d' % 20)
print('%x' % 20)
print('%f' % 1.11) # 默认保留 6 位小数
print('%.1f' % 1.11) # 取 1 位小数
print('%e' % 1.11) # 默认 6 位小数,用科学计数法
print('%.3e' % 1.11) # 取 3 位小数,用科学计数法
print('%g' % 1111.1111) # 默认 6 位有效数字
print('%.7g' % 1111.1111) # 取 7 位有效数字
print('%.2g' % 1111.1111) # 取 2 位有效数字,自动转换为科学计数法
print('%s' % 'hello world') # 字符串输出
print('%20s' % 'hello world') # 右对齐,取 20 位,不够则补位
print('%-20s' % 'hello world') # 左对齐,取 20 位,不够则补位
print('%.2s' % 'hello world') # 取 2 位
print('%10.2s' % 'hello world') # 右对齐,取 2 位
print('%-10.2s' % 'hello world') # 左对齐,取 2 位
# 输出:
# 24
# 20
# 14
# 1.110000
# 1.1
# 1.110000e+00
# 1.110e+00
# 1111.11
# 1111.111
# 1.1e+03
# hello world
# hello world
# hello world
# he
# he
# he
format 函数
str.format() 增强了字符串格式化的功能。基本语法是通过 {} 和 : 来代替以前的 %。format 函数可以接受不限个参数,位置可以不按顺序。
位置匹配:
- 不带编号,即“{}”
- 带数字编号,可调换顺序,即“{1}”、“{2}”
- 带关键字,即“{a}”、“{tom}”
格式转换:
- ‘b’ – 二进制。将数字以 2 为基数进行输出。
- ‘c’ – 字符。在打印之前将整数转换成对应的 Unicode 字符串。
- ‘d’ – 十进制整数。将数字以 10 为基数进行输出。
- ‘o’ – 八进制。将数字以 8 为基数进行输出。
- ‘x’ – 十六进制。将数字以 16 为基数进行输出,9 以上的位数用小写字母。
- ‘e’ – 幂符号。用科学计数法打印数字。用 ‘e’ 表示幂。
- ‘g’ – 一般格式。将数值以 fixed-point 格式输出。当数值特别大的时候,用幂形式打印。
- ‘n’ – 数字。当值为整数时和 ‘d’ 相同,值为浮点数时和 ‘g’ 相同。不同的是它会根据区域设置插入数字分隔符。
- ‘%’ – 百分数。将数值乘以 100 然后以 fixed-point(‘f’) 格式打印,值后面会有一个百分号。
左中右对齐及位数补全:
- <(默认)左对齐、> 右对齐、^ 中间对齐、=(只用于数字)在小数点后进行补齐
- 取位数“{:4s}”、”{:.2f}” 等
代码示例及其他:
import datetime
print('{}{}'.format('hello','world')) # 不带字段
print('{0}{1}'.format('hello','world')) # 带数字编号
print('{0}{1}{0}'.format('hello','world')) # 打乱顺序
print('{1}{1}{0}'.format('hello','world'))
print('{a}{tom}{a}'.format(tom='hello',a='world')) # 带关键字
print('{0:b}'.format(3))
print('{:c}'.format(20))
print('{:d}'.format(20))
print('{:o}'.format(20))
print('{:x}'.format(20))
print('{:e}'.format(20))
print('{:g}'.format(20.1))
print('{:f}'.format(20))
print('{:n}'.format(20))
print('{:%}'.format(20))
print('{} and {}'.format('hello','world')) # 默认左对齐
print('{:10s} and {:>10s}'.format('hello','world')) # 取 10 位左对齐,取 10 位右对齐
print('{:^10s} and {:^10s}'.format('hello','world')) # 取 10 位中间对齐
print('{} is {:.2f}'.format(1.123,1.123)) # 取 2 位小数
print('{0} is {0:>10.2f}'.format(1.123)) # 取 2 位小数,右对齐,取 10 位
print('{:<30}'.format('left aligned')) # 左对齐
print('{:>30}'.format('right aligned')) # 右对齐
print('{:^30}'.format('centered')) # 中间对齐
print('{:*^30}'.format('centered')) # 使用“*”填充
print('{:0=30}'.format(11)) # 还有“=”只能应用于数字,这种方法可用“>”代替
print('{:+f}; {:+f}'.format(3.14, -3.14)) # 总是显示符号
print('{: f}; {: f}'.format(3.14, -3.14)) # 若是 + 数,则在前面留空格
print('{:-f}; {:-f}'.format(3.14, -3.14)) # - 数时显示 -,与 '{:f}; {:f}' 一致
print('{:,}'.format(1234567890)) # 数字千位分隔符
print('{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}'.format(datetime.date.today())) # 日期时间格式化
字符串插值 F-strings
在Python 3.6.2版本中,PEP 498提出一种新型字符串格式化机制,被称为”字符串插值”或者更常见的一种称呼是F-strings,F-strings提供了一种明确且方便的方式将python表达式嵌入到字符串中来进行格式化:
# Python程序演示
# 字符串插值
n1 = 'Hello'
n2 = 'GeeksforGeeks'
# f告诉Python恢复大括号{}中两个字符串变量名和程序的值
print(f"{n1}! This is {n2}")
# 内联算法
print(f"(2*3)-10 = {(2*3)-10}")
要创建f字符串,请在字符串前添加字母”f”。字符串本身的格式与str.format()一样。F字符串为将python表达式嵌入字符串文字中进行格式化提供了一种简洁方便的方法。
拓展:字符串模板
string.Template,将一个string设置为模板,通过替换变量的方法,最终得到想要的string。
用法示例:
from string import Template
template_string = '$who likes $what'
s = Template(template_string)
d = {'who': 'Tim', 'what': 'KongFu'}
s_out = s.substitute(d)
print(s_out)
参考链接: